Fractionation
(Click to enlarge)
Principle
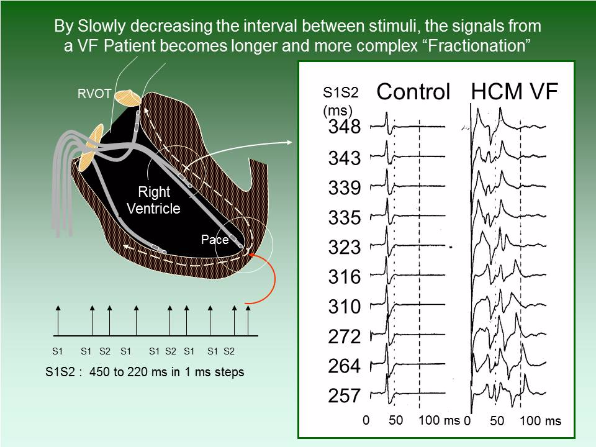
When the heart is paced at one point, activation is measured at other points within the heart. The pupose of fractionation is to see if the activation arrives evenly or comes as a sequence through multiple conduction paths.
Premature stimulation
The small potentials at the end of the electrogram, representing delayed conduction and disorgansation, are accentuated by decreasing the interval between a normal stimulus (S1) and an early stimulus (S2) known as the S1S2 interval. This is shown on the columns with electrograms obtained at increasingly shorter S1S2 intervals.
Increasing fractionationation in VF patients
The left hand column of electrograms are taken from a patient with a normal heart. These show no change as the S1S2 interval is decreased. The right hand column is taken from a patient with Ventricular Fibrillation (VF) and shows increasing length and additional peaks as the S1S2 interval is decreased. This implies highly disorgansed myocardium.
(Click image to enlarge)